Accrual reporting—recording the economic substance of transactions when they occur rather than when cash settlement happens—is fundamental to good decision making, transparency and accountability.
IFAC and CIPFA’s International Public Sector Financial Accountability Index collects, verifies, and analyzes current financial reporting bases and frameworks used by federal and central governments around the world. It also provides an overview of public sector reporting trends.
2021 Status Report
Analyzing data captured by the Index, this 2021 status report provides an update on the progress made since 2018 in implementing accrual-based reporting. It gives a snapshot of the position in 2020 and looks ahead by using currently available data to forecast the position in 2025 and provide indicative projections of the position in 2030.
The 2020 Index contains data from 165 jurisdictions, compared to 150 in the 2018 Index. The 2018 Index data has therefore been restated to provide comparability with the 2020 Index data.
The results paint a positive picture of accrual adoption efforts globally, with 30% of jurisdictions reporting on accrual in 2020 – up 6% since 2018.
Image
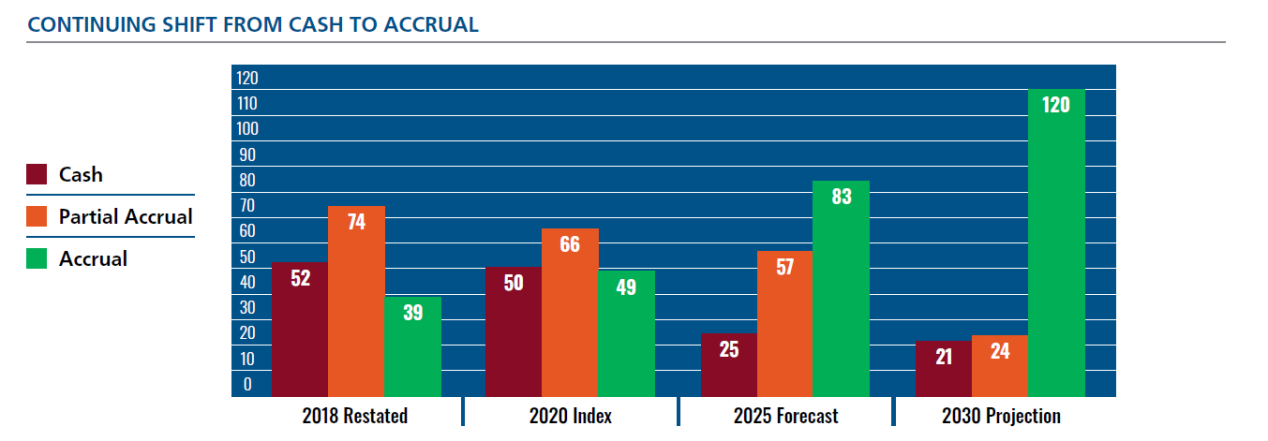
By 2025, 50% of Jurisdictions Will Report on Accrual
As reported in 2018, there is significant accrual adoption activity underway across all regions of the world.
The 2025 Forecast is based on reviews of the data supplied for the 2020 Index, as well as other available corroborative information to support predictions of where reform processes will have reached by 2025.
The regions expected to see the greatest increases in accrual adoption between 2020 and 2025 include:
- Africa: 9 jurisdictions (2 in 2020)
- Latin America and the Caribbean: 15 jurisdictions (9 in 2020)
- Asia: 17 jurisdictions (7 in 2020)
Image
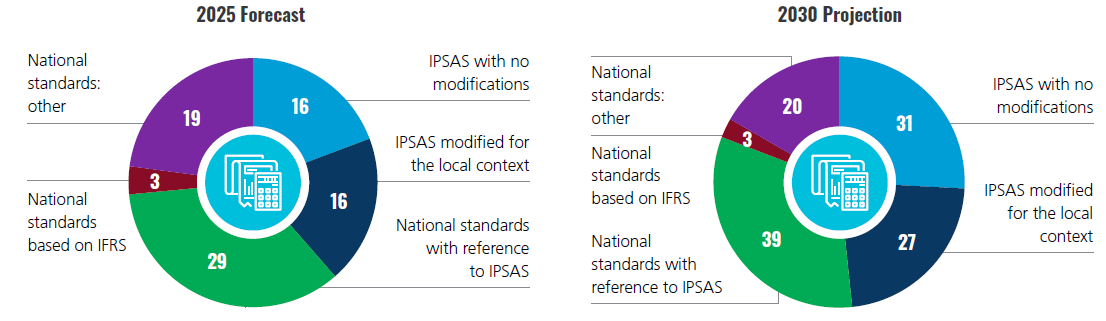
IPSAS Usage and Influence Will Increase
In 2025, 61 (73%) of jurisdictions forecast to report on accrual will make use of IPSAS: 16 will adopt IPSAS with no modifications; 16 will use IPSAS modified for the local context; and 29 will refer to IPSAS in developing their national standards. This means not only that the number of governments making use of IPSAS will have increased since 2018, but also that there will be an overall greater percentage of direct and indirect IPSAS implementation globally.
This trend is projected to continue, so that by 2030, 97 (81%) of the jurisdictions reporting on accrual are projected to be making use of IPSAS.
